When you consider the vast landscape of textiles, it’s important to recognize the diverse types of fabric that clothe you, decorate your home, and serve myriad other functions in daily life. Fabric isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s about the functionality and comfort that different materials provide for different purposes. From the traditional cotton and wool to the more innovative smart textiles and intelligent materials, you are surrounded by a world of textiles that cater to a variety of sensory and functional demands.
Understanding the properties of each type of cloth is essential for making informed decisions, whether you’re selecting attire for a special event, choosing upholstery for furniture, or picking out the appropriate materials for outdoor gear. Cotton, for instance, is lauded for its breathability and softness, making it a staple for casual wear. On the other hand, synthetic fabrics like polyester offer durability and moisture-wicking properties, which are crucial for active wear.
The influence of fabric on daily activities can be quite pronounced, from the effect of different types of textile fabric on spermatogenesis to the adsorption characteristics of disinfectants on various surfaces. Each type of material comes with its own set of characteristics that can impact its performance across different environments and uses. As you delve into the world of textiles, you’ll discover the importance of selecting the right fabric to suit your specific needs.
Natural Fabrics
Natural fabrics, sourced from plants and animals, are integral to the production of garments offering a range of textures, durabilities, and environmental advantages. When you choose natural textiles, you’re embracing materials like cotton, linen, and silk, which have been used to make clothing for thousands of years.
Cotton
Cotton fabric is one of the most popular natural fibers due to its breathability and ability to wick moisture, making it a staple for everyday wear. Your cotton garments are versatile, durable, and easy to care for, coming from the fluffy fibers surrounding the seeds of the cotton plant.
Linen
Made from the fibers of the flax plant, linen fabric is highly valued for its natural luster and coolness in hot weather. If you have linen textiles, you’ll notice they are stronger than cotton but can wrinkle easily due to the fabric’s lower elasticity.
Silk
Silk fabric is a luxurious, protein-based fiber produced by silkworms. As one of the softest natural fabrics, your silk garments provide a smooth, lustrous surface and are often reserved for high-end clothing due to their delicate nature and elaborate production process.
Wool
Comprising different types of animal hair, including wool fabric from sheep and cashmere from goats, protein fibers like these are known for their insulation properties. Your woolen clothing can keep you warm even when damp, and the fabric’s natural crimp helps it retain heat effectively.
Other Natural Fabrics
Beyond the most common natural fibers, there are other options including bamboo, known for its softness and antimicrobial properties, and hemp fabric, which boasts durability and environmental sustainability. These fabrics are gaining prominence in the textile industry as eco-friendly alternatives for your clothing and home textiles.
Synthetic Fabrics

Synthetic fabrics, derived primarily from petrochemicals, are essential in the modern textile industry due to their specific characteristics like durability, elasticity, and ease of care. They are widely used in different types of garments, offering varied benefits from water resistance to stretchability.
Nylon
Nylon, a synthetic fiber initially designed to mimic silk, is now fundamental in creating a variety of your garments. Nylon is famed for its exceptional strength and elasticity. It’s a go-to material for items requiring durability like outerwear and hosiery.
Polyester
Polyester fabric is renowned for its resistance to wrinkles and shrinking. Your everyday clothing, from shirts to dresses, often incorporates polyester due to its easy maintenance and longevity. Moreover, polyester’s ability to blend with natural fibers enhances fabric properties to meet diverse clothing necessities.
Acrylic
When you’re looking for wool-like warmth without the hefty price tag, acrylic is your synthetic fiber of choice. This lightweight material can often be found in your warm winter apparel, providing cozy comfort and resistance to moths and chemicals.
Spandex
Known for its incredible ability to stretch, spandex, also referred to as elastane, is what gives your stretch fabrics that much-needed flexibility. Spandex is typically used in sportswear and activewear, adding ease of movement and a better fit to the garments.
Other Synthetic Fabrics
Exploring beyond these common synthetics, you’ll discover rayon fabric and acetate, which offer silk-like smoothness and drape beautifully in your clothing. Their breathability makes them comfortable, yet they represent a more affordable option compared to natural silk. Various synthetic materials continue to be developed, enhancing the sustainability and performance of textiles across the board.
Weaving and Knitting
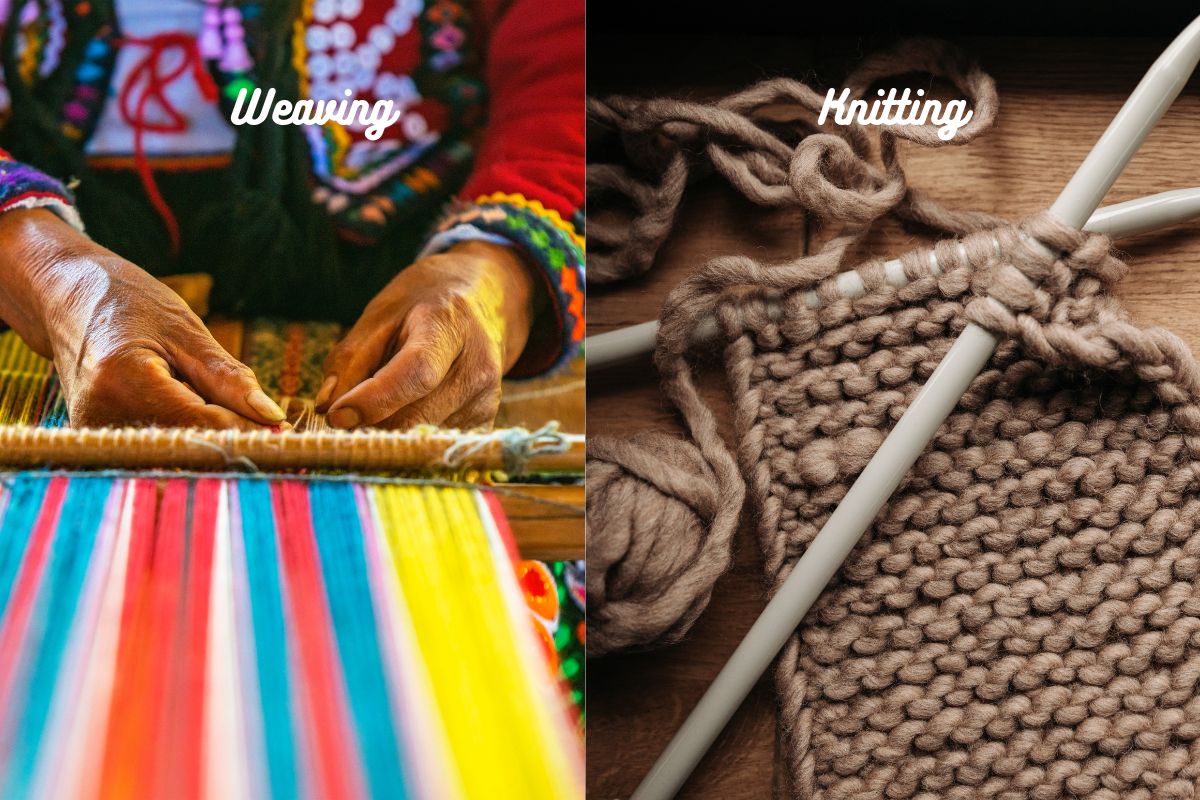

In the realm of textiles, your choice between woven and knitted fabrics impacts both the aesthetic and functional qualities of the finished product. Understanding the structure and properties of each type will guide your decisions, whether you’re choosing a durable denim for jeans or a stretchy jersey for a comfortable tee.
Woven Fabrics
Woven fabrics are created by interlacing two distinct sets of yarns at right angles to each other. This traditional technique produces fabrics with a plain weave—the simplest and most common weave pattern. For example, plain weave fabrics like muslin and gingham boast a balanced checkered pattern due to the 1:1 intertwining of warp and weft yarns.
- Denim, a robust textile, is often the go-to woven fabric for jeans. Its twill weave gives it a characteristic diagonal ribbing.
- Canvas is another sturdy fabric, commonly used for items demanding high durability, like tents and sails.
- Brocade and corduroy are examples of more specialized woven fabrics where patterns or wales are integral to their unique textures.
- Tweed, a woolen fabric, typically features a mix of colored threads to achieve its complex, often earthy appearance.
- For stiffening and reinforcing garments or book covers, tightly woven fabrics like buckram serve well.
In contrast to knitted fabrics, the tight interlock of yarns in woven textiles like plain weave fabric, tweed, or cambric (a light, closely woven fabric) limits stretch, offering a crisp, structured finish.
Knitted Fabrics
Knitted fabrics, on the other hand, are produced by looping yarns together, which gives them natural elasticity. Knit fabrics are preferred for garments that require some stretch, like hosiery or T-shirts.
- Jersey, a single knit fabric, is a mainstay for casual clothing due to its soft texture, stretch, and wrinkle resistance.
- Known for its smooth front and back texture, jersey knit fabric is often used in lighter apparel like tops and bedsheets.
- Textiles like stretch fabric refer to materials like spandex that are either knitted or woven with an elastic yarn to enhance stretchability.
Knitted fabrics like jersey knit provide comfort and ease of movement, making them ideal for active wear and casual attire. While sewing with knits, you might find the stretchiness challenging compared to the more stable woven alternatives.
Specialty and Luxury Fabrics

When you explore the world of specialty and luxury fabrics, you enter a realm where quality, rarity, and craftsmanship define the materials. These fabrics, ranging from leather and delicate laces to sumptuous silk varieties, offer you exceptional durability, comfort, and elegance for clothing, accessories, and even upholstery.
Leather and Animal Skins
Leather and animal skins are prized for their durability and versatility. Used in high-end garments, bags, and shoes, leather can range from the soft, plush feel of suede to the ruggedness of full-grain leather. Each type provides a distinct texture and aesthetic that can elevate the look and feel of your items. Exotic animal skins, such as snakeskin or crocodile, add a level of sophistication and luxury due to their unique patterns and rarity.
Lace and Embroidered
Lace and embroidered fabrics are synonymous with elegance and are often used in costumes, hats, and special occasion clothing. Featuring intricate patterns and designs, these fabrics are typically made from fine materials such as chiffon, tulle, or net. Embroidery can be done on a variety of base fabrics, incorporating materials like satin, velvet, or even organza, to create detailed and dimensional textures.
Silk Varieties
Silk is a hallmark of luxury with a rich array of varieties like satins, velvets, crepes, and georgettes. Each type offers a unique texture and aesthetic, from the lustrous sheen of charmeuse to the crisp drape of dupioni. Silk materials are widely chosen for their natural sheen, smoothness, and strength, making them ideal for high-quality dresses, blouses, and lining in fine clothing.
Other Specialty Fabrics
The category of other specialty fabrics encompasses a diverse range of textiles that includes velvet fabric, georgette fabric, and more. Fabrics like chenille offer a soft, tufted feel perfect for cozy upholstery, while tweed and boucle provide texture and depth for jackets and coats. Batik fabric is recognized for its wax-resist dyeing technique, which creates highly detailed, colorful patterns. Meanwhile, airy fabrics such as voile, gauze, and challis are ideal for lightweight, breathable clothing that doesn’t sacrifice style for comfort.
Fabric Care and Usage

Understanding the specific care requirements and applications of various fabrics can significantly enhance the longevity and appearance of your items. Whether you’re dealing with clothing, home textiles, or specialty fabrics, it’s essential to follow the appropriate care guidelines to maintain their quality.
Clothing and Apparel
Your wardrobe is an investment, and the right care can make a difference in how your clothing looks and feels over time. Denim, for instance, often requires less frequent washing and benefits from air-drying to preserve fit and color. Easy care finishing techniques can improve the sustainability and longevity of stretch denim garments. When caring for garments like shirts, dresses, and suits, always check the label for washing instructions and consider the material, as the needs can vary widely between cotton, polyester, and wool.
Home Textiles and Decor
From curtains to upholstery, the fabrics in your living space need regular maintenance to keep them looking their best. Bed linens, for example, should be washed often, but with gentle detergents to maintain their softness. Curtains might require different cleaning methods based on their materials, such as dry cleaning for silk or machine washable synthetics. If you’re handling stain removal, always test a small, inconspicuous area of the fabric first to ensure that the cleaner won’t cause damage.
Industrial and Technical Uses
Industrial fabrics are designed for specific functions, such as fire resistance or water repellency, and require specialized care to maintain these properties. When managing the care for technical fabrics, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines meticulously. The use of incorrect cleaning agents or techniques can compromise the fabric’s integrity and functionality.
Care and Maintenance
Caring for your bags, shoes, and hats often starts with proper storage – keep them in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. For shoes, use a conditioner made for the material they’re constructed from, whether it’s leather or synthetic, to keep them supple and prevent cracks. Stain removal from bags and hats should be approached with caution; use targeted remedies such as a suede eraser for specific materials. Implementing regular sewing checks can aid in catching tears early, preventing further damage to your favorite pieces.
Always refer to the individual care labels on clothing and textiles for best results, and when in doubt, consult with a professional cleaner, especially for items of significant value or with challenging materials.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations

When exploring the realm of textile production, your consideration for both sustainability and ethical practices plays a critical role. Natural fibers, like cotton and wool, often have a lower environmental impact during growth but can require significant water and land resources. To mitigate this, organic options with strict ecological and social standards are accessible.
Regarding synthetic materials, while they offer durability and versatility, they come with a notable environmental cost due to petroleum dependence and challenges in end-of-life disposal. The production of these materials can result in polluting emissions and the garments themselves can shed microplastics during washing.
Integrating sustainability in this aspect involves:
- Opting for recycled synthetic materials.
- Seeking out certifications indicating low-impact production.
Ethical considerations in garment production encompass:
- Ensuring fair labor practices.
- Supporting fair trade initiatives.
- Preventing exploitation across the supply chain.
Real-world examples include the environmentally friendly bark cloth suited for sustainable fashion and the ethical fashion project collaborative, which focuses on ethical implications within products.
| Aspect | Action Item |
| Natural Fibers | Favor organic and responsibly sourced materials. |
| Synthetic Materials | Choose recycled and recyclable options. |
| Ethical Production | Support brands practicing fair labor and trade agreements. |
Your awareness and choice of ethically produced and sustainable fabrics not only reduce the environmental impact but also contribute to a more conscientious fashion industry. Remember, each purchase is a vote for the practices you want to support.
Fabric Types and Definitions
When you explore the realm of textiles, you’ll find a variety of fabric types each with unique properties and uses. Here’s a brief breakdown:
- Cotton: A natural fiber known for its breathability and versatility, cotton is widely used in both clothing and home textiles.
- Silk: A luxurious natural fiber, silk is prized for its smooth texture and lustrous appearance, often used in high-end garments.
- Linen: Linen is another natural fiber, recognized for its durability and coolness, making it a popular choice for summer wear.
- Wool: Harvested from animals, wool is a warm and cozy fabric ideal for colder climates and winter garments.
- Polyester: A synthetic fiber that is durable and often blended with other fibers to enhance its characteristics, such as wrinkle resistance.
- Nylon: Known for its strength and elasticity, nylon is commonly used in sportswear and hosiery.
- Spandex: Highly stretchable, spandex is integrated into fabrics that require elasticity, such as workout attire.
- Rayon: A semi-synthetic fiber that imitates the feel of silk, linen, and cotton, and is often used for its draping qualities.
Each type of fabric comes in various weaves and weights, which influence the texture, strength, and drape. For example, denim is a sturdy, woven cotton fabric, while satin, which can be made from silk or synthetic fibers, has a glossy surface and a dull back.
Understanding these fabric types and their properties allows you to make informed choices for your wardrobe, home décor, and other fabric-related projects.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we address common inquiries regarding fabric types, characteristics, and considerations for use. You’ll find precise information that can help you better understand fabrics and make informed choices in their application.
What are the distinguishing characteristics of natural vs synthetic fabrics?
Natural fabrics, like cotton, silk, and wool, come from plants and animals and are praised for their breathability and softness. Conversely, synthetic fabrics such as polyester and nylon are human-made, offering durability and moisture-wicking properties.
Which fabric materials are most commonly used in the apparel industry?
Cotton is widely used for its comfort and versatility, while polyester is favored for its strength and wrinkle resistance. These materials, alongside blends like cotton-polyester, are staples in clothing production.
How do you identify fabric types based on textile weave patterns?
Plain weave is characterized by its simple over-and-under pattern, while twill shows a distinctive diagonal rib. Satin weave offers a smooth surface, indicative of its pattern where the weft yarn floats over several warp yarns.
What are the most sustainable fabric choices for eco-friendly fashion?
Organic cotton, hemp, and Tencel are sustainable options that reduce environmental impact. They are produced using methods that conserve resources and avoid harmful chemicals.
Can you describe the different properties of woven, knit, and non-woven fabrics?
Woven fabrics are structured, with a grid-like pattern that resists stretching. Knit fabrics have interlocking loops, making them stretchy and comfortable. Non-woven fabrics, such as felt, are bonded together without knitting or weaving, resulting in a more felt-like appearance.
What factors should be considered when choosing fabric for upholstery?
Durability, as measured by the double rub count, is crucial for upholstery that withstands wear and tear. Consider also the fabric’s stain resistance, colorfastness, and if it complements the room’s function and aesthetic.